
Photographic crosssection of the abdomen from the Visible Human Male. Download Scientific Diagram
Cross-sections are two-dimensional, axial views of gross anatomical structures seen in transverse planes. They are obtained by taking imaginary slices perpendicular to the main axis of organs, vessels, nerves, bones, soft tissue, or even the entire human body.

Abdomen and pelvis normal anatomy eAnatomy
Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): Muscles of the Abdomen - Cross Section. When viewed in cross section the relative positions of the lateral muscles can easily be seen. The tendon of the external oblique passes superficial to the rectus abdominus while the tendon of the transversus abdominus passes deep. The tendon of the internal oblique splits to.

Transverse Cross Section of Abdomen Diagram Quizlet
Abdominal computed tomography (CT) is a type of medical imaging procedure used to diagnose and monitor internal stomach issues, like cancer, bowel obstruction, and abdominal pain. Radiographers suggest an abdominal CT scan to look for the following: Hernia Cause of a fever Kidney stones Appendicitis Cause of blood in the urine
Schematic Cross Section through Abdomen (T12) code 6000.16 Altay Scientific
EXERCISE: Abdomen Cross Section Section 3: Anatomy of the Pelvis (15:19) EXERCISE: Pelvis Cross Section Section 4: Anatomy of Musculoskeletal (29:45) Slides: Anatomy of Chest, Abdomen & Pelvis Week 11: Test (20 Questions) Week 12: CT Artifacts Section 1: Artifacts - Appearance, Cause & The Fix (23:45).

CT scan of abdomen (crosssection view). Download Scientific Diagram
Abdomen - Axial cross section: Omental bursa; Lesser sac, Omental foramen; Epiploic foramen Intestinal tract: 2 illustrations of gross anatomy to introduce the different parts of the digestive tract. Gastrointestinal tract: Oesophagus, Stomach, Small intestine, Large intestine Stomach: anatomical images of the gastric anatomy, from the serous.
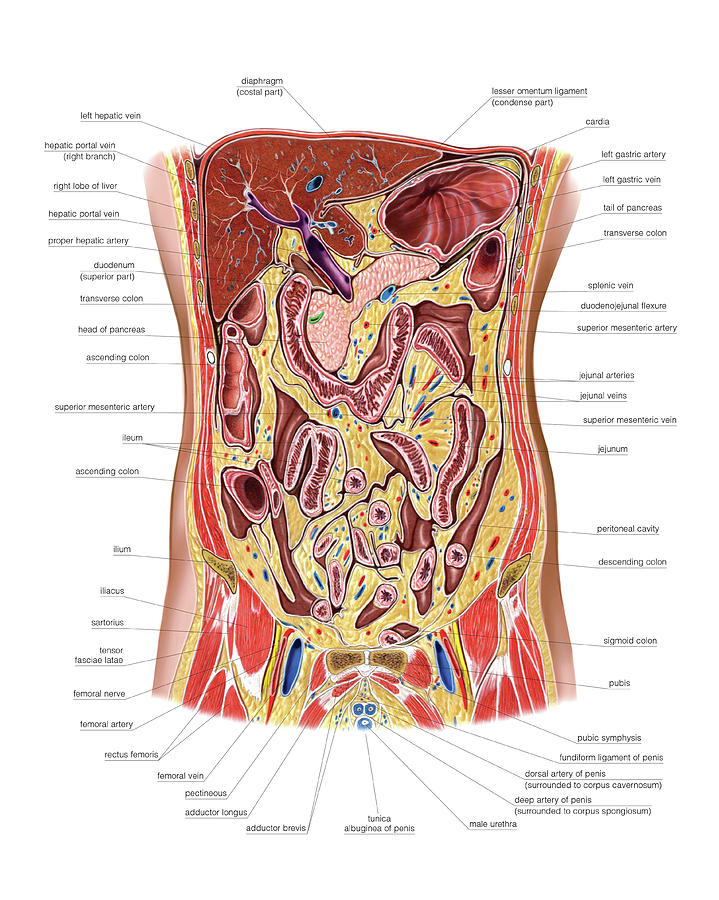
The Abdomen Photograph by Asklepios Medical Atlas Pixels
The abdominal wall surrounds the abdominal cavity, providing it with flexible coverage and protecting the internal organs from damage. It is bounded superiorly by the xiphoid process and costal margins, posteriorly by the vertebral column and inferiorly by the pelvic bones and inguinal ligament.. The abdominal wall can be divided into two sections: anterolateral and posterior abdominal walls.

Posterior Aspect of the Abdominal Viscera and Retroperitoneum Oncohema Key
️ LEARN MORE: This video lesson was taken from our Cross-Sectional Anatomy and Pathology course. Use this link to view course details and additional lessons.

Schematic Cross Section of Abdomen at Middle T12 Anatomy Liver , Falciform ligament , Superior
Stomach Cross-section Food enters the body through the mouth. Inside, mechanical breakdown begins immediately as it is chewed and mixed with saliva. This breakdown continues as the food travels.

Abdominal Wall Anatomy Of The Abdomen Learn Surgery
This session covers Sectional anatomy of Abdomen , Pelvis.Cross Section as well as Mid Sagittal section Sections covered.Gross Specimens compared with CT Sca.
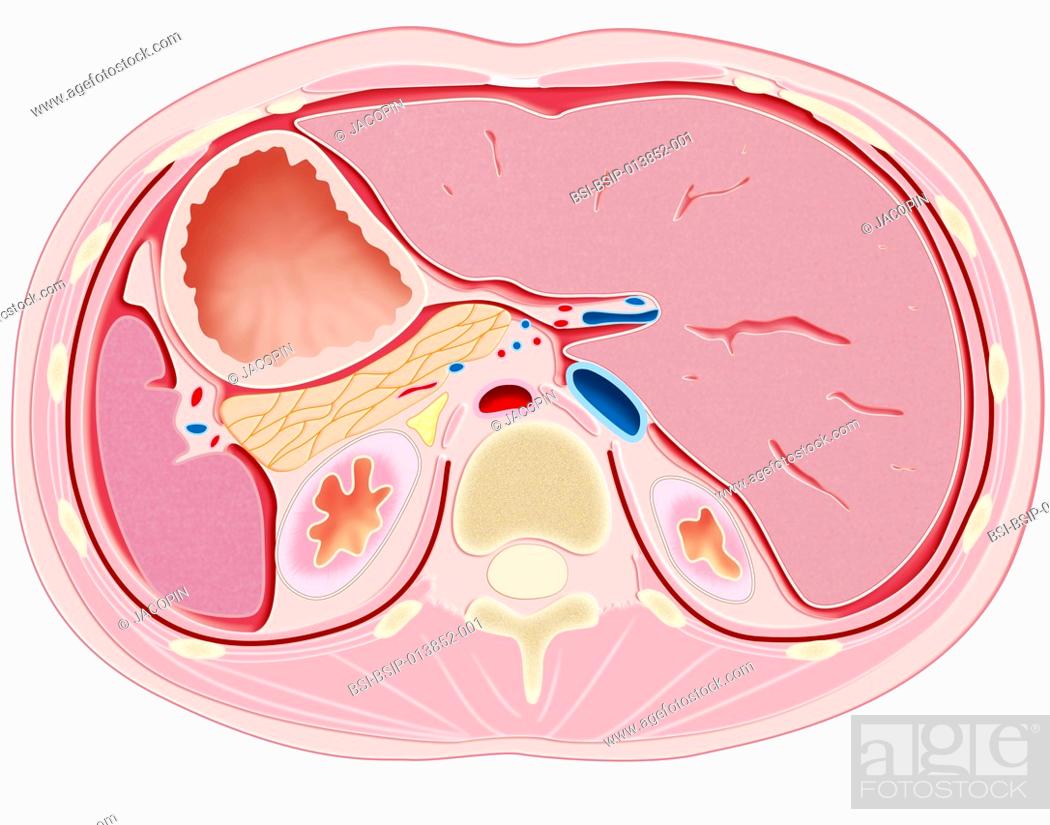
Crosssection illustration of organs in the abdomen at T12L1, Stock Photo, Picture And Rights
This MRI abdomen axial cross sectional anatomy tool is absolutely free to use. Use the mouse scroll wheel to move the images up and down, or alternatively, use the tiny arrows (→) on both sides of the image to navigate through the images.
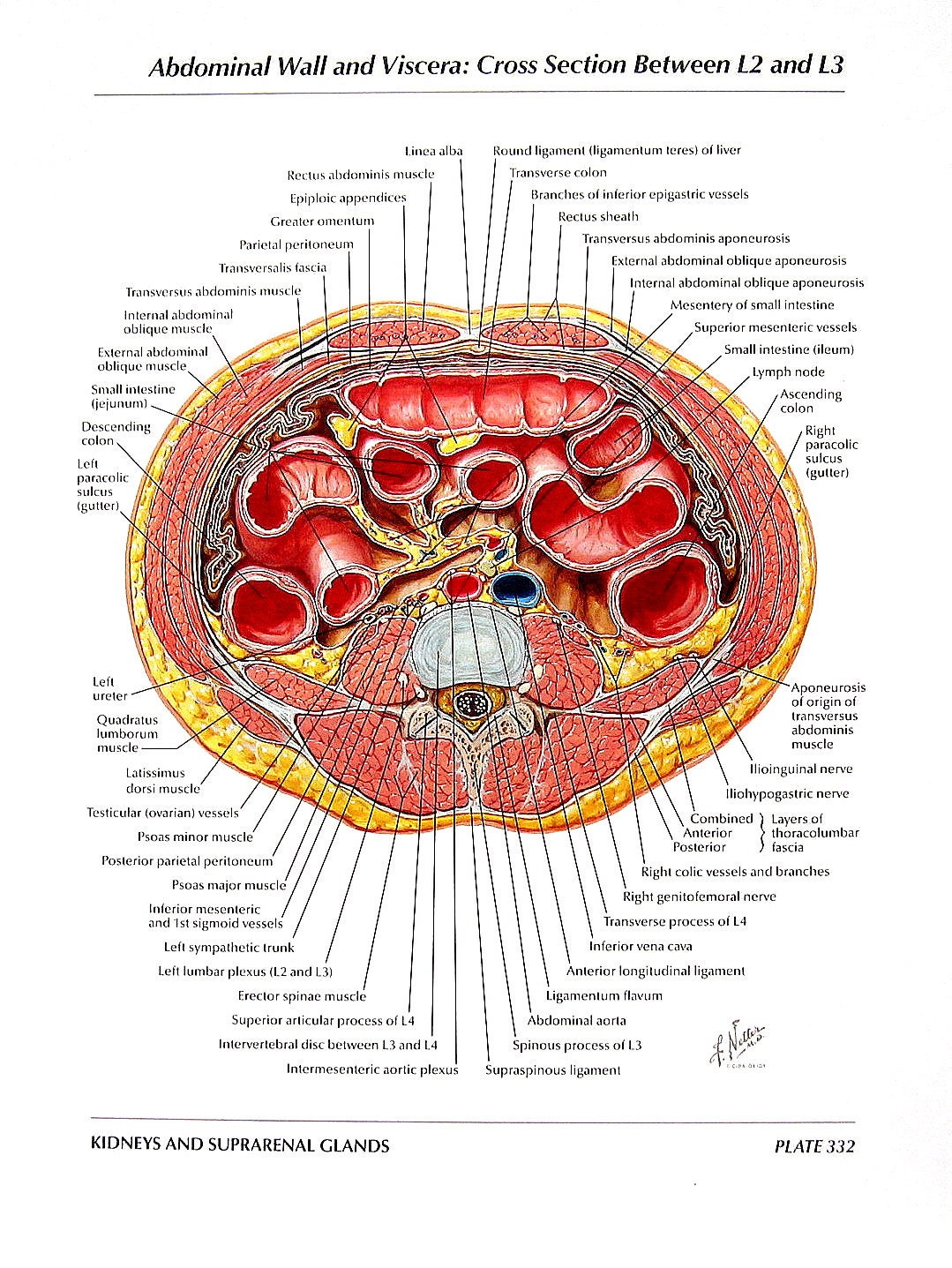
Anatomy Print Abdominal Walls and Viscera Cross Section
anatomical parts. The Visible Human Project® is an outgrowth of the NLM's 1986 Long-Range Plan. It is the creation of complete, anatomically detailed, three-dimensional representations of the normal male human body. Complete cross-sectional images of representative male cadaver. The male was sectioned at one millimeter intervals.

Normal Anatomy of the Abdomen Saggital and Cross Sectional View
Abdomen Cross Section - luc.edu

Axial View of the Abdomen TrialExhibits Inc.
FIGURE 4-3 Transverse cross section of abdomen at mid-lumbar spine level. Internal oblique, external oblique, and transverse abdominis come together at anterior of abdominal wall to form a common aponeurosis, which continues to form the rectus sheath surrounding rectus abdominis.

Axis Scientific Anatomy Model of Abdominal Cross Section at T12 Offers View of Thorax at T12
Anatomical structures of the abdomen and pelvis are visible as interactive labeled images. Cross sectional anatomy: MDCT of the abdomen and pelvis An enhanced (portal venous phase - 70 seconds) multidetector computed tomography was performed on a healthy subject in axial plane with coronal and sagittal reformatted images.

Abdominal Cross Section (T12) Diagram Quizlet
Videos Quizzes Abdomen Peritoneum and peritoneal cavity Stomach Spleen Pancreas Liver and gallbladder Small intestine Large intestine Kidneys, ureters and adrenal glands Pelvis Perineum Urinary bladder and urethra Female reproductive organs Male reproductive organs Blood vessels Innervation Lymphatics Sources Related articles Abdomen and pelvis
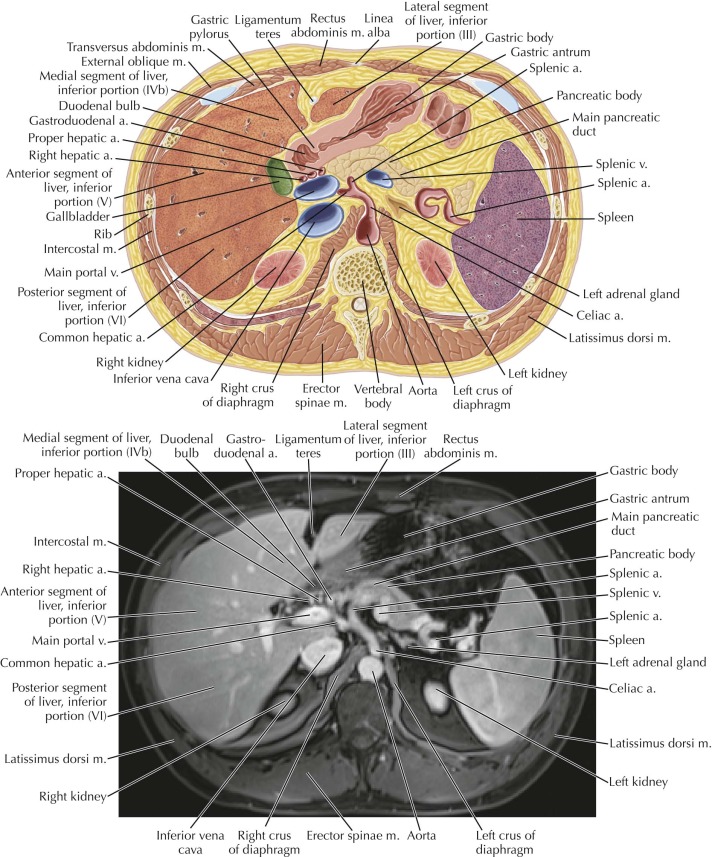
Abdomen Radiology Key